Laya Kiani has a degree in Pharmaceutical Chemistry from the University of Guelph, which she combines with a keen passion for business and marketing. She has shifted her focus toward the business side of health care, driven by a desire to make significant impacts in the health science sector. Dedicated to continuous learning and professional growth, Laya continues to build her career on the pillars of innovation, integrity and inspiration, striving to bridge the gap between scientific discovery and practical health-care solutions through smart marketing and business strategies.
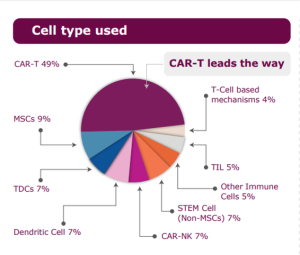
Source: Alliance for Regenerative Medicine, April 2024 Sector Snapshot, Advances in Engineered Cell Therapy
The Research and Markets report estimates that the worldwide market for regenerative medicine was valued at US$30.44 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to US$168 billion by 2034 (all figures in U.S. dollars). This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.80 per cent over the forecast period from 2024 to 2034. Funding primarily flows from venture capital, public offerings, partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions. Thus, the strategic infusion of capital into regenerative medicine is not just a financial decision—it is a profound commitment to pioneering a healthier future for all.
The investment landscape in regenerative medicine is vibrant and rapidly evolving. With significant capital influx, groundbreaking technological advancements and strong investor confidence, the field is set to continue its trajectory of innovative growth. For venture capitalists (VCs), staying informed about the latest scientific and market trends will be key to making strategic investment decisions in this promising area.
Some of the key trends, technologies and emerging markets in the future of regenerative medicine include:
Cell therapy and CAR T leads the way
Cell therapy and immunotherapy have emerged as revolutionary treatments capable of harnessing the body’s immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells, offering new hope for patients across various cancer types. From immune checkpoint inhibitors to CART-cell therapy, these innovative approaches represent a significant leap forward in cancer management and potential cures. Notably, CAR T therapies, exemplified by Novartis AG’s Kymriah CAR T therapy, have garnered substantial attention, with U.S. Food & Drug Administration accelerated approval in May 2022 for treating adult relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
These therapies utilize engineered receptors to specifically target cancer cells. Presently, six CAR T-cell therapies for blood cancers are approved in the U.S. and Europe, with numerous others, including non-CAR T approaches, advancing through clinical pipelines. Notably, nine of the top ten explored indications in cell therapy focus on blood cancers, indicating a concentrated effort in this domain. With approximately 200 drugs in development, 13 are projected to surpass Kymriah and Yescarta’s revenues, contributing an additional $5 billion or more by 2024.
Convergence of biotechnology and information technology
Regenerative medicine is increasingly influenced by the integration of biotechnology with various information technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, cloud computing, the Internet of Things and blockchain. These technologies enhance the research and development activities within regenerative medicine by accelerating the discovery and optimization of new biomolecules, cells and tissues. They also support the design and creation of complex, functional biological structures, improve the monitoring and evaluation of the safety and efficacy of regenerative medicine therapies, and foster the development of new health care delivery models and platforms. This includes supporting digital health ecosystems, patient-centred and decentralized care, and facilitating data sharing and collaboration among various stakeholders.
Precision medicine and genomic sequencing
Driven by progress in genomic sequencing, precision medicine is advancing its transformation of health care. Techniques such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and single-cell sequencing in precision medicine are yielding deeper understanding of the genetic foundations of diseases. According to GenEngNews.com, the race in genomics that began in 2022 is evolving into what resembles an ultramarathon.
Gene editing and CRISPR
In the 11 years since its inception, CRISPR Therapeutics has made significant strides in advancing precision medicine. A notable example of this progress is the development of CRISPR-CasΦ (phi), the latest gene-editing tool following CRISPR Cas9. CasΦ highlights the capability of CRISPR therapeutics to perform precise genomic edits, from correcting mutations that cause diseases to adjusting gene expression. The applications of CRISPR therapeutics extend beyond treating genetic disorders, including agricultural enhancements that contribute to combating climate change. Despite these advancements, ethical and regulatory challenges persist. Regulatory bodies are struggling to find the right balance between innovation, safety and ethical concerns, which could significantly shape the future trajectory of CRISPR-based therapies, for better or worse.
Regeneration X – 3D bioprinting and regenerative medicine
3D bioprinting, combined with regenerative medicine, is transforming the field of tissue engineering by offering innovative solutions for the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues. Revenues in tissue engineering are projected to rise from $4.4 billion in recent figures to $8.9 billion by 2028, a growth spurred by significant advances in bioprinting technology and a growing demand for regenerative treatments.
These techniques are crucial in addressing the severe shortage of donor organs by creating personalized tissues and organs, which also reduces the risk of transplant rejection. Bioprinting has the potential to solve the organ shortage issue and provide revolutionary drug testing platforms. Organ-on-a-chip models allow scientists to simulate the functions of certain organs and evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the suggested medications in an ethical manner. Fewer failed clinical trials, coupled with more accurate medication efficacy expectations, could completely alter the drug development process.
Multi-faceted approach to funding in regenerative medicine:
Considering the financial landscape, regenerative medicine companies can tap into diverse capital sources, including:
- Funds from governmental and non-profit organizations.
- Investments from corporate venture funds focused on strategic gains.
- Collaborative agreements with pharmaceutical companies.
- Acquisitions through strategic partnerships and mergers.
- Generating revenue by licensing non-essential technologies or offering consultancy and lab services.
- Other opportunities: academic funding, loans, crowdfunding and peer-to-peer financing, and incubators and accelerators.
Moreover, regenerative medicine startups should streamline their operations by focusing on essential activities and reducing distractions. They should consider:
- Continuing technology development within academic partnerships.
- Downsizing infrastructure and workforce to reduce overheads.
- Prioritizing funding towards core projects only.
Success in this field also hinges on the ability to collaborate effectively and share resources. Outsourcing certain development processes to trusted partners can enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness. Amid the financial constraints facing today’s emerging regenerative medicine firms, adopting collaborative and cost-efficient business models alongside alternative financing methods can significantly improve their chances of success. By doing so, these companies may increase their appeal to VC firms looking to invest in promising areas like cell therapy, a field comparable in transformative potential to the pioneering technology of humanized monoclonal antibodies that once revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry.
Investment decision factors
Surveys conducted by The International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy (ISCT) in 2018 and 2021 aimed to query investors about their perceptions and behaviours regarding the development of companies and technologies in the cell and gene therapy (CGT) sector. In 2018, projections for investment in CGT were conservative compared to the actual growth observed. By 2021, it was evident that the landscape of opportunities in CGT was more attractive to health-care investors than initially expected.
Gene-editing technologies draw investors’ attention
A survey asked investors to identify and rank their top three most attractive CGT technologies. Gene-editing technologies, induced pluripotent stem cell-derived therapies, and engineered natural killer cells emerged as the most influential in driving positive investment. The strong appeal of gene editing is reflected in the significant capital these companies have raised. Meanwhile, engineered natural killer cells offer an attractive alternative to T-cell-based therapies, supported by promising early-stage clinical data. However, ex vivo gene-modified cell therapies ranked lowest due to commercial challenges, despite regulatory approval for products like Strimvelis and Zynteglo. Manufacturing complexities and high costs have created hurdles for patient-derived therapies to gain commercial traction.
Clinically significant data as the primary investment driver
When ranking the top factors influencing investment decisions, “clinically significant data” was the most influential factor. “Platform Technology” was the only other factor widely recognized as highly important. The data underscore that impactful clinical results remain the primary motivator for investors considering CGT companies. Growing awareness of manufacturing challenges has also raised the profile of “Manufacturing and Scale-up” issues, while “Management Experience” emerged as a significant influence between 2018 and 2021. Interestingly, “Company Valuation” became less critical, indicating a shift in investor focus toward overall company quality rather than merely finding the best price.
Barriers to CGT investment
In the 2021 survey, the biggest barrier was competition from other drug modalities, followed closely by challenges in manufacturing, scaling up and clinical development complexity. Safety concerns, which were the top barrier in 2018, dropped to fourth place as investors became more comfortable with CGT product safety. Notably, cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity management for CAR T products have improved. The rise of bispecific antibodies has also posed challenges to cell therapy products, particularly for hematological malignancies. Developers will need to address these issues to raise future equity.
Late-stage success with allogeneic cell therapies may help counter the lower-cost appeal of regenerative medicine in a rapidly evolving field that promises to revolutionize the treatment of various diseases and injuries. Developing and commercializing regenerative therapies, however, involves significant challenges. These include scientific innovation, clinical validation, regulatory approval and market access.
The vibrancy of the investment landscape in regenerative medicine is characterized by substantial capital inflows, technological breakthroughs and strong investor confidence, all of which propel the field toward continued innovative development. VCs, in particular, are encouraged to keep abreast of the latest scientific developments and market dynamics to make informed decisions.
Key technological trends shaping the future of regenerative medicine include advanced cell therapies like CAR T, which are changing cancer treatment paradigms, and the convergence of biotechnology with information technology, enhancing R&D through tools like AI, and big data. Additionally, innovations in 3D bioprinting are paving the way for next-generation tissue engineering.
For regenerative medicine companies, strategic collaboration and efficient capital management are crucial for navigating the complexities of development and commercialization. Leveraging partnerships, focusing on core projects, and exploring alternative funding sources are strategies that can substantially enhance a company’s potential for success and attractiveness to investors.
The regenerative medicine sector is at a pivotal juncture, with the capacity to transform medical treatments and significantly improve patient outcomes. Continued investment and innovation will unlock further breakthroughs, positioning regenerative medicine at the forefront of medical science and health-care development.
***********
If you would like to read more on this topic, here are some recommended articles and reports:
Profiles of exciting new companies and in-depth coverage of larger funding rounds, with a focus on clinical trial results, special reports, and enterprise stories. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/fierce-biotech-fundraising-tracker-24
The challenges and strategies related to the development and commercialization of tissue engineered medical products (TEMPs). https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00095/full
Stem Cell/Regenerative Medicine in Canada: Current State and Future Prospects https://www.ihe.ca/download/stem_cell_regenerative_medicine_in_canada_current_state_and_future_prospects.pdf
Guest
Latest posts by Guest (see all)
- Regenerative immunotherapy: Hope for chronic autoimmune diseases - September 16, 2025
- Canada’s regenerative revolution: Why AI is the catalyst - September 4, 2025
- Summer by Design: A launchpad for future entrepreneurs and industry scientists - August 14, 2025






Comments